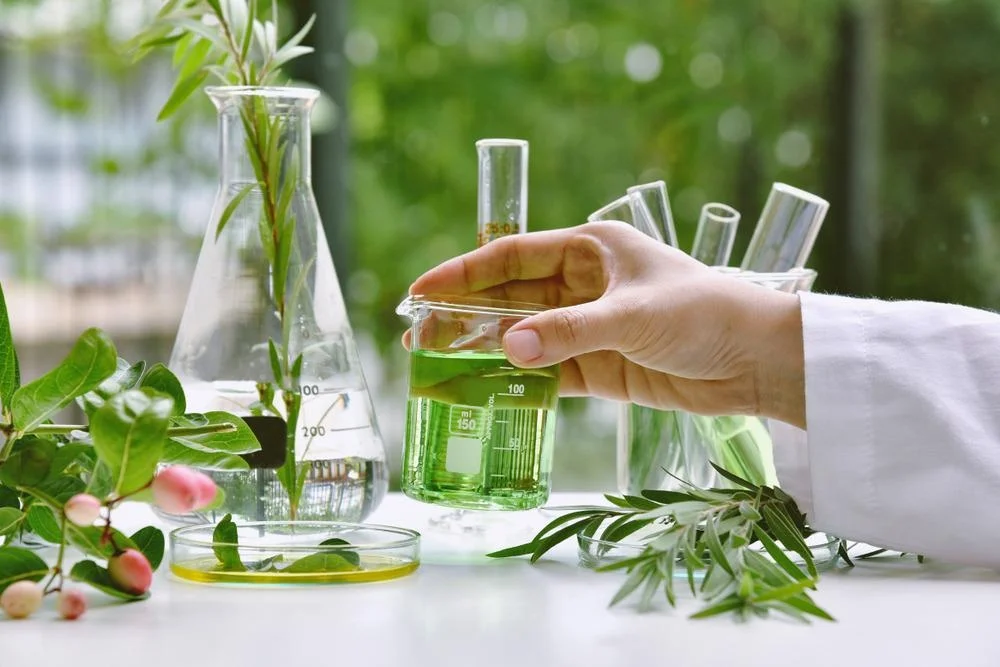
For thousands of years, humans have turned to plants as a primary source of medicine. Long before modern laboratories and synthetic drugs, ancient civilizations relied on leaves, roots, bark, and flowers to treat illnesses, relieve pain, and improve overall well-being. Today, despite remarkable advances in pharmaceutical science, plant discovery for medicines remains one of the most important and promising areas of research in modern healthcare.
In fact, a significant proportion of today’s prescription drugs are either directly derived from plants or inspired by plant-based compounds. As antibiotic resistance rises, chronic diseases increase, and the demand for safer, more sustainable treatments grows, scientists are once again looking to nature’s vast botanical library for solutions.
This blog explores how plant discovery for medicines works, why it matters, notable success stories, challenges involved, and the future of plant-based drug development.
The Historical Importance of Medicinal Plants
The relationship between plants and medicine is deeply rooted in human history. Ancient medical systems such as Ayurveda, Traditional Chinese Medicine (TCM), Unani, and Indigenous healing practices all relied heavily on plant-based remedies.
Some historical examples include:
- Willow bark, used in ancient Greece, which later led to the development of aspirin
- Opium poppy, used for pain relief, which gave rise to morphine
- Cinchona tree bark, the original source of quinine for malaria treatment
These early discoveries laid the foundation for modern pharmacology and demonstrated that plants contain powerful bioactive compounds capable of treating serious diseases.
Why Plant Discovery for Medicines Still Matters Today
Despite advances in synthetic chemistry, plants remain an invaluable source of new drugs. There are several reasons why plant discovery for medicines continues to be critical:
1. Rich Chemical Diversity
Plants produce a wide range of unique chemical compounds to protect themselves from pests, diseases, and environmental stress. These compounds often interact with human biological systems in beneficial ways.
2. Natural Drug Leads
Many modern drugs are based on plant compounds that serve as “lead molecules,” which scientists modify to improve effectiveness and safety.
3. Rising Drug Resistance
Antibiotic resistance and drug-resistant cancers are growing global threats. Plant-derived compounds offer new mechanisms of action that can help overcome resistance.
4. Growing Demand for Natural Therapies
Consumers increasingly prefer plant-based and natural medicines, driving research and investment in botanical drug discovery.
The Process of Plant Discovery for Medicines
Modern plant-based drug discovery is a systematic and scientific process that combines traditional knowledge with advanced technology.
1. Ethnobotanical Research
Scientists often begin by studying how indigenous communities use plants for healing. Traditional knowledge helps narrow down which plants are most likely to contain medicinal compounds.
2. Plant Collection and Identification
Botanists carefully collect plant samples and accurately identify species to ensure reproducibility and safety.
3. Extraction and Isolation
Plant materials are processed to extract chemical compounds. These extracts are then separated to isolate individual active ingredients.
4. Biological Screening
Extracts and compounds are tested in laboratories to evaluate their effects on cells, bacteria, viruses, or disease models.
5. Optimization and Drug Development
Promising compounds are refined to improve potency, reduce toxicity, and enhance absorption in the human body.
6. Clinical Trials
Before approval, plant-derived drugs must undergo rigorous clinical trials to prove their safety and effectiveness.
Famous Medicines Discovered from Plants
Plant discovery for medicines has already produced some of the world’s most important drugs.
Cancer Treatments
- Paclitaxel (Taxol): Derived from the Pacific yew tree, widely used in cancer chemotherapy
- Vincristine and Vinblastine: Extracted from the Madagascar periwinkle, used to treat leukemia and lymphoma
Heart and Blood Pressure Medications
- Digoxin: Derived from foxglove plants, used to treat heart failure
- Reserpine: From Rauwolfia serpentina, used to manage high blood pressure
Pain Management
- Morphine and Codeine: From the opium poppy, still essential for pain relief
These examples highlight how plant discovery for medicines directly impacts millions of lives worldwide.
Medicinal Plants and Modern Diseases
Plant-based research is playing a growing role in addressing today’s most pressing health challenges.
Cancer
Many plants contain compounds that inhibit tumor growth, induce cancer cell death, or enhance the effects of existing therapies.
Infectious Diseases
With antibiotic resistance on the rise, plant-derived antimicrobial agents are being explored as alternatives or supplements to traditional antibiotics.
Diabetes
Numerous medicinal plants help regulate blood sugar levels and improve insulin sensitivity, supporting diabetes management.
Neurological Disorders
Plants with neuroprotective properties are being studied for conditions such as Alzheimer’s, Parkinson’s, and depression.
Challenges in Plant Discovery for Medicines
While promising, plant-based drug discovery is not without challenges.
1. Biodiversity Loss
Deforestation and climate change threaten many medicinal plant species before their potential can be explored.
2. Complex Chemistry
Plant extracts contain hundreds of compounds, making it difficult to identify which ones are responsible for therapeutic effects.
3. Sustainability Issues
Overharvesting medicinal plants can harm ecosystems and local communities.
4. Regulatory Hurdles
Plant-derived drugs must meet the same strict regulatory standards as synthetic medicines, which can be time-consuming and expensive.
Technology’s Role in Modern Plant Discovery
Advances in technology are revolutionizing plant discovery for medicines.
Artificial Intelligence (AI)
AI helps analyze massive datasets to predict which plant compounds are most likely to be effective against specific diseases.
Genomics and Metabolomics
These tools allow scientists to understand how plants produce medicinal compounds and how they interact with the human body.
Biotechnology
Plant compounds can now be produced in laboratories using genetically engineered microorganisms, reducing the need for large-scale harvesting.
Ethical and Environmental Considerations
Responsible plant discovery must respect both nature and indigenous knowledge.
- Benefit-sharing agreements ensure local communities are compensated
- Sustainable harvesting practices protect ecosystems
- Conservation programs preserve endangered medicinal plants
Ethical approaches help ensure long-term access to nature’s medicinal resources.
The Future of Plant Discovery for Medicines
The future of plant discovery for medicines is incredibly promising. As global health challenges become more complex, nature offers a vast and largely unexplored resource for innovation.
Key future trends include:
- Increased integration of traditional medicine and modern science
- Greater use of AI-driven drug discovery
- Expansion of plant-based therapies for chronic diseases
- Stronger focus on sustainability and conservation
With over 300,000 plant species worldwide, scientists have only scratched the surface of nature’s medicinal potential.
Conclusion
Plant discovery for medicines remains a cornerstone of modern healthcare, bridging ancient wisdom with cutting-edge science. From life-saving cancer drugs to everyday pain relief, plants have shaped medicine in profound ways — and their role is far from over.
As research methods improve and awareness of sustainability grows, plant-based drug discovery will continue to unlock new treatments, offering hope for safer, more effective, and environmentally responsible healthcare solutions.